Abstract
Background: HAS is widely used in clinical practice for a variety of haematological, renal, neurological, respiratory and metabolic conditions. A United Kingdom shortage in 2015 prompted a demand management guideline incorporating the American Society for Apheresis (ASFA) indications 1 and GSTFT criteria 2 for other indications.
Objectives:The objective of this study was to evaluate the indications for HAS usage following the introduction of the GSTFT demand management guideline.
Methods: We audited HAS usage from August 2015 to March 2023 at GSTFT. Data was entered in SPSS version 20, with categorical variables described as frequencies and percentages.
Results:
4816 patients received HAS during the study period, totaling 21,231 infusions.
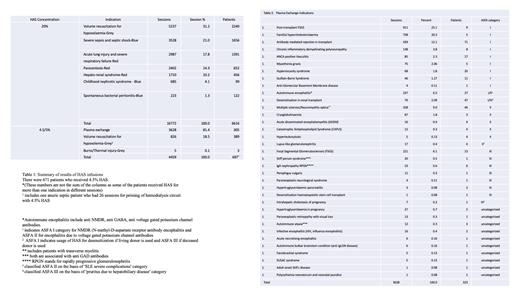
We recorded 16,772 (79%) infusions for 20% HAS in 4,145 patients. The indications for 20% HAS included; volume resuscitation for hypovolaemia 5237 (31%), severe sepsis/septic shock 3528 (21%), acute lung injury and severe respiratory failure 2987 (18%), paracentesis 2402 (14%), hepatorenal syndrome 1710 (10%), childhood nephrotic syndrome 685 (4.1%) and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis 223 (1.3%) (Table 1). According to GSTFT criteria infusions were recorded in the following indication categories: Red 7099 (42.3%), Blue 4436 (26.4%) and Grey 5237 (31.2%).
A total of 4459 (21%) infusions were recorded for 4.5 and 5% HAS. A total of 3628 (81%) infusions were used for plasma exchange (PEX) in 305 patients; 2817(76.99%) ASFA category I, 445(12.03%) category II, 290(7.97%) category III and 92 (2.5%) for indications not specified according to ASFA; 826 infusions (18.5%) were for volume resuscitation for hypovolaemia (Grey indication) in 389 patients, the remaining 5 infusions (0.1%) were in 3 patients for burns and thermal injuries (Table 1).
Major indications for PEX included post-transplant focal segmental glomerulosclerosis 911 infusions (20%) in 9 patients, familial hypercholesterolaemia 738 infusions (16%) in 5 patients, antibody mediated rejection 439 infusions (10%) in 71 patients (Table 2).
Conclusions: This report provides a rare long term retrospective review of total albumin usage in a large UK tertiary referral center. The majority (97.5%) of PEX HAS indications were within ASFA guidelines. Aside from apheresis the main indication for HAS was volume resuscitation, a grey indication, where evidence is weak.
REFERENCES
(1) Padmanabhan A, Connelly-Smith L, Aqui N, Balogun RA, Klingel R, Meyer E, Pham HP, Schneiderman J, Witt V, Wu Y, Zantek ND, Dunbar NM, Schwartz GEJ. Guidelines on the Use of Therapeutic Apheresis in Clinical Practice - Evidence-Based Approach from the Writing Committee of the American Society for Apheresis: The Eighth Special Issue. J Clin Apher. 2019 Jun;34(3):171-354. doi: 10.1002/jca.21705. PMID: 31180581
(2) Yazdani MS, Retter A, Maggs T, Li P, Robson MG, Reid C, Holmes P, Garood T, Robinson SE. Where does the Albumin go? Human Albumin Solution usage following the implementation of a demand management programme. Transfus Med. 2017 Jun;27(3):192-199. doi: 10.1111/tme.12406. Epub 2017 Apr 3. PMID: 28370709.
Disclosures
Harrington:Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding.